GAT Simple Paper
GAT General consists of three sections:
1. English
2. Quantitative
3. Analytical Reasoning
English
This section contains the following types of questions:
- Vocabulary (Synonyms, Antonyms, Analogies, Sentence Completion)
- Word Choice (with respect to grammar)
- Word Choice (with respect to vocabulary)
- Grammar
- Summary Completion
- Reading Comprehension
Quantitative
This section contains questions from following topics:
- Basic Algebra
- Word Problems
- Arithmetic and Logic
- Geometry
Analytical Reasoning
This section contains following types of questions:
- Collecting given information
- Conclusion; after gathering given information
- Inference from the given information and conclusion
GAT Sample Paper
Section-A (English)
Synonyms
1. RESTIVE
(A) Restful
(B) Restless ![]()
(C) Crucial
(D) Pause
2. CRAVEN
(A) Cowardly ![]()
(B) Laziness
(C) Politely
(D) Arrogant
Antonyms
3. PERFIDY
(A) To impure
(B) Thoroughness
(C) Purification
(D) Loyalty ![]()
4. EFFICACY
(A) Strange
(B) Well-known
(C) Inefficiency ![]()
(D) Effectiveness
Analogies
Recognize the relation between the given pair of words (in capital). And, select the pair of words from the given options that best expresses a relationship similar to that in capital pair of words.
5. CARPENTER: SAW
(A) athlete: runner
(B) assembly: member ![]()
(C) mason: wall
(D) reaper: sickle
6. MENDACITY: HONESTY
(A) courage: cravenness ![]()
(B) wickedness: lie
(C) money: wealth
(D) acclaim: truthfulness
Summary Completion
Complete the following summary with suitable answers
When you can measure (7)__________ you are speaking about, and express it(8)_________ numbers, you know something (9)________ it, when you cannot measure it; when you cannot (10)_______ it in numbers, your knowledge is of a meager and unsatisfactory kind; it may be the beginning of knowledge, but you have (11)___________ in your thoughts, advanced to the stage of science.
7.
(A) when
(B) what ![]()
(C) where
(D) whom
8.
(A) in ![]()
(B) to
(C) from
(D) with
9.
(A) for
(B) within
(C) about
(D) nearly ![]()
10.
(A) tell
(B) ask
(C) say
(D) express ![]()
11.
(A) immature
(B) scarcely ![]()
(C) arrogantly
(D) lack
Grammar
12. Anas, Umar and I________ going.
(A) am
(B) was
(C) are ![]()
(D) have been
13. If I________time, I would have purchased it yesterday.
(A) had had
(B) would had ![]()
(C) would have
(D) had have
Reading Comprehension
Read the following paragraphs carefully and choose the correct answers from the options given below
These huge waves wreak terrific damage when they crash on the shores of distant lands or continents. Under a perfectly sunny sky and from an apparently calm sea, a wall of water may break twenty or thirty feet high over beaches and waterfronts, crushing houses and drowning unsuspecting residents and bathers in its path.
How are these waves formed? When a submarine earthquake occurs, it is likely to set up a tremendous amount of shock, disturbing the quite waters of the deep ocean. This disturbance travels to the surface and forms a huge swell in the ocean many miles across. It rolls outward in all directions, and the water lowers in the centre as another as another swell looms up. Thus a series of concentric swells are formed similar to those made when a coin or small pebble is dropped into a basin of water. The big difference is in the size. Each of the concentric rings of basin water traveling out toward the edge is only about an inch across and less than a quarter of an inch high. The swells in the ocean are sometimes nearly a mile wide and rise to several multiple of ten feet in height.
Many of us have heard about these waves, called “tsunami”. Nothing was done about tsunamis until after World War II. An underwater earthquake in the Aleutian Islands could start a swell that would break along the shores and cause severe damage. These waves travel hundreds of miles an hour, and one can understand how they would crash!
14. One surprising aspect of the waves discussed in the passage is the fact that they
(A) are formed in concentric patterns
(B) often strike during clear weather ![]()
(C) arise under conditions of cold temperature
(D) are produced by deep swells
15. It is believed that the waves are caused by
(A) seismic changes ![]()
(B) concentric time belts
(C) underwater earthquakes
(D) storms
16. The normal maximum width of the waves is approximately
(A) one mile
(B) five miles
(C) five feet
(D) ten feet ![]()
17. Nothing was done about the waves until
(A) deaths occurred
(B) a solution was found
(C) millions of dollars worth of damage was incurred
(D) the outbreak of World War II ![]()
18. The movement of the waves has been measured at a speed of
(A) 1 mile an hour
(B) 50 miles an hour
(C) 100 miles an hour
(D) more than a hundred miles an hour ![]()
Analytical Reasoning – GAT Sample Paper
GAT Analytical Reasoning (Sample Questions, Answers and Explanation)
Question (19-23) 7 persons live in a street, having houses in line. Consider the following:
1. A lives in the corner’s house
2. C is between E and G
3. There is I house between D and F
4. F is neighbor of G
5. There are two houses between A and G
19. Who lives in the second corner?
(A) B
(B) C ![]()
(C) D
(D) E
(D) F
20. Who lives in the middle?
(A) C
(B) D
(C) E
(D) F
(E) G ![]()
21.Who lives between B and G?
(A) C
(B) D
(C) E
(D) F ![]()
(E) G
22. ________is neighbor of A?
(A) B
(B) C
(C) E
(D) F
(E) G ![]()
23. There are ________ houses between B and E?
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) 3 ![]()
(E) 4
GAT Quantitative Section
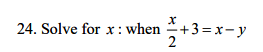
(A) x=y+2
(B) x = y +4
(C) x = y +6
(D) x = 2y+4
(E) x = 2y+6 ![]()
25. The straight line 2x+3y+4=0 touches the x-axis at?
(A) x=-2 ![]()
(B) x = 2
(C) x=1
(D) x=-1
(E) x=0
26. 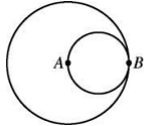
Consider the larger circle and an inner circle. Point A is center of larger circle. If the line AB (not drawn) is 7 cm in length, then find the area of larger circle.
(A) 94 cm
(B) 112 cm
(C) 136 cm
(D) 154 cm ![]()
27. 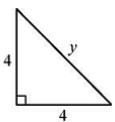
The value of y in the above triangle is?
(A) √16
(B) 16
(C) √32 ![]()
(D) 32
